In 1824, the process of greenhouse effect was first noticed by a French physicist named Joseph Fourier. He was the first scientist to consider that the atmosphere of our planet may be similar to that of an insulator that reflects the earth’s radiation back toward its surface. The average temperature on the earth is about 57oF. In the absence of greenhouse effect, this temperature may come down as low as -2.2oF, which is an icy cold temperature. Venus and Mars are two other planets that also show signs of greenhouse effect. The surface of Venus is surrounded by an atmosphere of carbon dioxide gas which is a greenhouse gas and warms up the temperature. Let’s learn about it in greenhouse effect for kids!
If there were no greenhouse gases in our atmosphere, all life on earth would burn to a crisp in daytime and freeze up during hours of darkness.
The light coming down from the Sun is in the form of electromagnetic radiation. This solar radiation is in the form of:
- Ultraviolet light (UV);
- Infrared Rays (IR); and
- Visible light
- The UV light is normally invisible to the human eye. They have shorter wavelengths as compare to visible light.
- The IR is an invisible light. It has a longer wavelength than light rays (visible light). About 50 percent of the radiation from the Sun consists of infrared light. Besides, a large portion of radiation given off by surfaces of warm objects is in the form of infrared rays.
- When solar radiation is blocked by the clouds in the atmosphere of the earth, it falls on the earth’s surface as ‘diffused light’.
- When solar radiation is not blocked by the atmospheric clouds or other air particles, it falls down on earth as ‘sunshine’.
What is the Greenhouse Effect and how does it work
The earth is surrounded by a layer of atmosphere. The atmospheric layer is composed of different gases and like a ‘protective shield’, they keep our atmosphere warm in order to support life on earth. This layer of atmosphere traps the solar radiation inside. The continuous sunlight heats up the earth’s surface. As a result, this heated surface emits infrared rays and these emitted-rays have a longer wavelength as compare to the sunlight absorbed by it. Now that most of these rays are reflected by the atmosphere back to the lower part of the atmosphere while some of these rays are again absorbed by the earth. Like so, the solar radiation is locked in the atmosphere and raise up the temperature. Actually, the molecules present in these gases regulate the temperature and do not allow the heat of the sun to break out. This phenomenon is referred to as greenhouse effect. The word ‘greenhouse’ comes from the greenhouse garden center for nurturing plants. Likewise, these atmospheric gases are known as greenhouse gases because they do not block the solar radiation (in the form of visible light) but traps the long-wave radiation emitted by the earth’s surface and prevent them from escaping into space.

Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming | Greenhouse Effect for Kids
- The earth’s atmosphere reflects back 30 percent of the solar radiation coming down from the sun and 70 percent of it is allowed to reach on earth.
- Almost half of the solar energy present in the atmosphere is absorbed by the surface of the earth. The other half is either absorbed by the atmosphere or reflected back by it and re-radiate it toward the earth.
- As temperature of the earth’s surface reaches 255 K, the wavelength of infrared rays emitted by it ranges from 4 to 100 μm. Greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere tend to absorb rays of such wavelengths. Atmosphere is composed of different layers and greenhouse gases present in the upper layer tend to absorb the heat emitted by the lower layers. These gases do not absorb all of the heat released by the lower layers. When gases (on the upper layers) absorb this heat, once more they radiate it to the lower layers as well as the layers above them. As a result, the temperature below these layers gets warmer. Like so, as the amount of greenhouse gases increase, the absorbing power of atmospheric layers also rise and thus they radiate more heat downwards leading to a rise in surface temperature.
What are the main Greenhouse Gases | Causes of Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gases have the capacity to release as well as absorb infrared rays. The primary gases present in the atmosphere are nitrogen, oxygen and argon. They make up almost 99 percent of the total atmospheric gases. But these gases are not labeled as ‘greenhouse gases’ because unlike greenhouse gases, they do not have the capability to take in and afterwards release infrared radiation.
The greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are:
Water vapor | It is invisible and forms by the process of evaporation. Its weight is less than that of air. It contributes about 36 to 70 percent to the greenhouse effect.
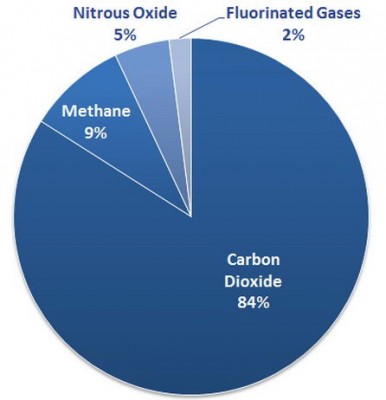
Carbon dioxide (CO2)| It is a gas in the atmosphere. When all the living organisms exhale air (in the process of respiration), carbon dioxide is given off. Likewise, plants also emit carbon dioxide during night. The concentration of this gas in the air is about 0.04 percent. More than 50 percent of the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is released by the vehicles and other means of transport on earth. It contributes about 9 to 26 percent to the greenhouse effect. During photosynthesis, plants and trees inhale carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Thus, we can diminish the concentration of carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) in the air by planting more and more trees.
Methane (CH4) | It is also a gas at normal temperature. Methane is the most important ingredient of natural gas. It exists deep inside the earth but also emerges from beneath the soil as atmospheric methane. It contributes about 4 to 9 percent to the greenhouse effect.
Laughing gas or Nitrous oxide (N2O) | It is a colorless gas at normal temperature but has sweet aroma. Like many other oxides of nitrogen, it is also one of its oxides and turns into nitric oxide when reacting with oxygen in the air.
Ozone (O3) | It is a gas with a fairly blue color but has a bitter smell. Three molecules of oxygen combine to form ozone and hence an allotrope of oxygen atom. It contributes about 3 to 7 percent to the greenhouse effect.
Clouds also play a vital role in greenhouse effect. They reflect some of the solar radiation from the sun back into space and also reflect the long-wave radiation (emitted by the earth’s surface) downwards and thus keeps the atmospheric temperature warm.


Leave a Reply